Shunning the sun is NOT fun!
That’s what the mounting evidence from various reports on vitamin D deficiency are trying to tell us.
New research on Vitamin D is now clear that bone health is only one of the many many benefits that vitamin D bestows on us.
Vitamin D deficiency now affects more than 70% population of the world. India alone has more than 700 million people living under the threat of vitamin D deficiency.
Contents
Incidence of Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is indiscriminate in nature as it may strike you irrespective of your age, gender, race and geography.
Well mostly indiscriminate, as your age, color and location DO have a bearing on how much Vitamin D you are making. 🙂
According to a report, more than 70% adults (age < 50) in the US and Europe are vitamin D deficient or insufficient.
Similarly, even with the abundant availability of sunlight, Vitamin D deficiency is becoming endemic in India with more than 70% people falling under the deficiency radar.
| Country | Percentage of people with low or insufficient Vitamin D level (<50 nmol/L (<20 ng/mL)) | |||
| Children | Adults | Pregnant/Lactating women | Elders(age>50) | |
| USA | 16% | 35% | 33% | 34% |
| India | 75-80% | 66% | 96% | 91% |
| China | 40% | 46% | 69% | 36% |
| Australia | 28% | 31% | 48% | 45% |
| Britain | 35% | 47% (in winter) | 35% | 52% |
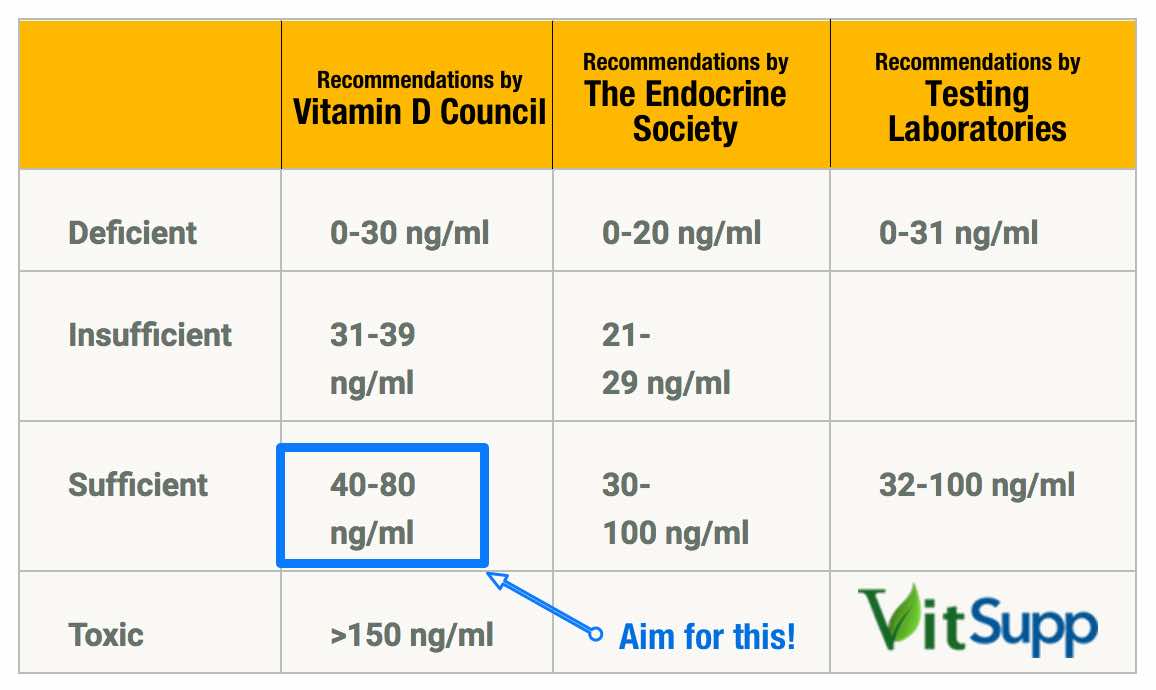
Vitamin D Level Chart
Vitamin D level is a measurement of a metabolite called 25-hydroxyvitamin D (also known as 25(OH)D, a form of vitamin D produced in the liver). There is no standard test method to evaluate the vitamin D level. Levels indicated as normal by one method may be read differently by other.
We recommend following the Vitamin D Council Guidelines.
* Serum concentrations of 25(OH)D are reported in both nanomoles per litre (nmol/L) and nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL).
** 1 nmol/L = 0.4 ng/mL
What is the Normal range of Vitamin D Levels?
While different health agencies are setting different values, I recommend the values being promoted by the Vitamin D council. As seen in the image above, 40-80 ng/ml is good.
REMEMBER: how much vitamin D you need to supplement to reach this level will vary for each person.
For example, lets say Susie just got tested and has a level of 12, and her husband Joe has levels of 15, as you can see both are deficient with similar levels of Vitamin D. However Susie may need to supplement less or more than Joe depending on her body’s needs to reach the healthy level of say 50 ng/ml. There is no way to find this out except, by testing your Vitamin D status regularly until you reach your goal.
REMEMBER: Too much supplementing of synthetic Vitamin D can be toxic! So when supplementing, KEEP TESTING! Of Course if you opt for Vitamin D via sunshine, you don’t need to worry about too much sunshine, the body knows what to do with too much of that. 🙂
Vitamin D RDA
As per the United States Institute of Medicine, the RDA (recommended dietary allowances) of vitamin D are:
| Age group | RDA (IU/day) |
| Infants 0–12 months | 400 (10 μg/day) |
| 1–70 years | 600 (15 μg/day) |
| 71 + years | 800 (20 μg/day) |
| Pregnant/Lactating women | 600 (15 μg/day) |
(Conversion: 1 µg = 40 IU and 0.025 µg = 1 IU)
NOTE: This is not a hard and fast dose. For many people the requirement is so high that these doses may not budge their Vitamin D levels. Then they have to opt for higher doses. Once again, KEEP TESTING when supplementing vitamin D.
How to establish Deficiency with Vitamin D Tests?
Vitamin D deficiency is a growing concern worldwide and hence in some of the western nations the recommended daily intake has been doubled for newborns and kids. To measure the level of vitamin D in blood, the 25- hydroxyvitamin D test is performed.
As the awareness of vitamin D deficiency is gaining momentum, the demand for Vitamin D test is also skyrocketing.
The alternative names for vitamin D test are:
- 25-OH vitamin D test,
- Calcidiol,
- 25-hydroxycholecalciferol test.
Vitamin D Blood Test
The blood test that measures the level of vitamin D is called a 25(OH)D blood test or 25- hydroxyvitamin D test. It is well known and most accurate way to measure the blood level of vitamin D in your body. The result of this test can tell you whether your body is getting too little, excessive, or just the right amount of vitamin D. People usually opt for this test when:
- They are low in calcium or phosphate.
- Experience symptoms like bone weakness or pain.
- Worried about osteoporosis after going through menopause.
- Have undergone gastric bypass surgery.
- Have fat malabsorption.
- Before beginning the drug therapy for osteoporosis.
Basically, this test is to tell you how severely you are deficient in vitamin D as excessive vitamin D level is a rarity. After the test result is out, remember these numbers:
- 50+ indicates a good level of Vitamin D
- 30-50 means that you are a bit on the lower side of vitamin D. You should be spending more time in sunlight. Eating vitamin D rich foods and supplementing vitamin D might help you.
- Below 30 means that you are very deficient and serious action need to be taken to bring those levels up! Better you consult with your doctor and ask if higher doses of Vitamin D are required.
I urge each individual to take up this test at least once as optimistic assumption that your vitamin D level is in healthy range may be quite risky.
Vitamin D Test Price in India
In India it costs somewhere around INR 1500 which is a bit on the higher side for socioeconomically underprivileged Indians.
Signs & Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
The biggest problem with Vitamin D deficiency is that there may be no outward sign or symptom of the same.
My friend was having bouts of dizziness, with general weakness and pains all over. She was also depressed and could cry at the slightest provocation. turns out she had low Vitamin D along with a host of other deficiencies too.
Anyway, nobody ever has just a single deficiency, its usually an array of deficiencies. So if you do have Vitamin D deficiency, do test more, as there may be more.
Coming back to symptoms, some people observe symptoms that are subtle while others have no symptoms at all. However, irrespective of visible signs, vitamin D deficiency can pose a serious health risk. And don’t expect your doctor to diagnose a Vitamin D deficiency from symptoms. It is best to go for a yearly or 6 monthly checkup of Vitamin D via blood test.
The list of Signs & Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is linked to many critical health ailments including different types of cancer (breast cancer, bowel cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, etc.) and coronary heart diseases. Recognizing the early signs can save you from many problems. Here is the list:
Excessive head sweating
This is one of the early clues for a person low in vitamin D. Excessive sweating on forehead occurs for both new borns and adults. If you are sweating off your head while your activity level remains normal, it’s time to check your D-efficiency.
Depression
Many studies have suggested that People with low level of vitamin D are more susceptible to be depressed than those with adequate levels. Vitamin D is responsible for increasing the levels of dopamine and serotonin (feel good hormones) and are also involved in numerous brain processes. Thus, it is known to play vital role as anti-depression agent.
There is no conclusive evidence that suggest how exactly vitamin D helps cure depression. One of the latest theory suggests that some of the vitamin D receptors are found in the brain area where development of depression occurs. Hence, vitamin D deficiency is often linked with depression and other mental illness.
According to a study, a person with low level of vitamin D is 11 times more susceptible to be depressed than those who have normal or adequate levels.
Weight gain
The actual connection between Vitamin D and weight gain is not known to many. Multiple studies have pointed out vitamin D to have a significant role in weight gain. A study by The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (AJCN) stated that “Women whose blood levels of vitamin D reached healthy levels through supplementation during a diet and exercise program lost more weight than those whose blood levels did not.”
NOTE: Not everybody will lose weight by supplementing Vitamin D. Weight Loss MAY accompany Vitamin D supplementation but only if you are low in it.
Low immunity
According to NCBI, apart from vitamin D’s classic role in bone health it has also found to be potent enough in providing immunity against the foreign and invasive organism. It influences more than 3000 genes (out of 25000) of your body and enables your body to produce more than 200 antimicrobial peptides to fight against wide range of infections.
Low immunity can be due to many reasons, but the Vitamin D hormone certainly plays its part in boosting the immune system as much as it regulates the expression of genes that influence your immune system to fight and destroy bacteria and viruses.
Joint pain
There can be many reasons for joint pain (also known as arthritis or arthralgia). However, if you are experiencing unexplained joint pain then you must consult your doctor for vitamin D deficiency. As suggested by many studies Vitamin D deficiency in the blood may cause pain and weakness in bones and muscles (including in the joints). It is more prominent in knee and back area especially in postmenopausal women and elders.
Unexpected weakness and fatigue
Chronic fatigue is the early warning signs of vitamin D deficiency but it is often overlooked as potential cause. Vitamin D is a critical hormone which helps muscle cells contract to withstand external force, consequently aids to muscle strength. Hence, low level of vitamin D are always linked to muscle pain and fatigue.
Vitamin D is a critical hormone and its receptors are present all over the body. 1,25-hydroxyvitamin D (A by-product of vitamin D) contributes to muscles strength. While getting metabolized, vitamin D enters the muscle cells and help them contract (A property of muscles tissue to withstand external force). So, any deficiency will result in weakness in muscles and unexpected fatigue.
In one case, a man who complained of chronic daytime fatigue was found to have a low blood level of vitamin D at 18.4 ng/mL. After undergoing vitamin D supplementation, the man was reported to have complete resolution of daytime fatigue.
Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms in Adults
Once again, excessive sweating from the forehead and noticeable but unexpected weakness are the classic signs of vitamin D deficiency in adults.
Adults with inadequate vitamin D level are prone to get depressed quickly as Vitamin D aids increase the levels of serotonin and dopamine (feel-good neurochemicals) in the brain that keep you happy. Some adults experience subtle joints and muscles ache or pains in the bones, known as osteomalacia.
Increased blood pressure may also be an indication of inadequacy of vitamin D. According to a study, low levels of Vitamin D are tied to testosterone dip in healthy men.
Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms in Men
Men with inadequate or low level of vitamin D are more likely to be
- Obese,
- Physically inactive
- Low in testosterone and
- Depressed.
- They may experience pain in bone specially in joints.
According to a study on 2,300 men by the researchers from the University of Manchester (UK), People with vitamin D deficiency were more than twice prone to chronic widespread pain than those who had good level of vitamin D.
Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms in Women
The benefits of vitamin D as proven by tons of research are quite loud and clear but the signs that indicate you are low in this hormone are a bit quieter. Women with low level of vitamin D may have following symptoms:
- Difficulty in thinking clearly.
- Excessive perspiration with normal activity.
- Unexplained fatigue
- Muscle weakness.
- High blood pressure
- Sleepiness
- Low immunity
- Stress fractures
- Sadness
Vitamin D Deficiency in Pregnancy
In pregnancy, monitoring the status of vitamin D become critical as now, there are two patients to consider. During the latter half of pregnancy, a mother needs increased level of vitamin D as the bone growth and ossification are most prominent during this phase.
The low level of Vitamin D has been linked with many reproductive disorders, including preterm birth, miscarriage, and hypogonadism. Several researches have indicated that inadequacy of vitamin D in breast milk may exert harmful effects on a new-born including low offspring birth weight. vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy may also lead to increased risk of infections and cesarean section.
According to a study around 50% of UK adults are deficient in vitamin D which has been linked to osteoporosis, gestational diabetes and 40% increased preeclampsia risk in pregnant women.
Vitamin D Deficiency in Children
In a couple of years, the number of children, who are deficient in vitamin D have increased by 200%. Vitamin D is crucial for children’s health as it helps absorb the sodium and provides the children with strong bones and healthy muscles. Vitamin D deficiency can wrack havoc to your child’s health as a couple of them listed here suggest:
- Children, who do not get enough vitamin D through breast milk (at the time of birth) are most likely to develop rickets later in childhood.
- Lower levels of vitamin D can keep the children from reaching their genetically programmed height and peak bone mass.
- Maternal vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy may cause low serum calcium in the new-born and generate defective tooth enamel at later stage.
- Some studies also claim that vitamin D deficient children are more likely to develop Crohn’s disease, type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis later in life.
- Vitamin D is vital from immune system and hence the children with low level of vitamin D are more prone to flue and other infections as compared to those with high levels.
Calcium and Vitamin D Deficiency Symptoms
Calcium and Vitamin D are two most important nutrients for bone health. We need to get enough of them to build strong and dense bone and to keep the bone healthy as we age.
Vitamin D is crucial for calcium absorption by our body. Though we can get calcium from many food sources such as dairy products, yogurt and cheese but we need vitamin D to enable our body to absorb it.
Calcium has got its presence throughout our body and any deficiency will have severe impact on our health. If you suspect yourself to be low in calcium just lookout for these primary symptoms:
- Muscle cramps and muscle ache (especially in thighs and arms) serve as the initial alarm that you are getting low in calcium.
- Loss of sleep (or you may call insomnia) is another sign of calcium deficiency. Sometimes people may fall asleep but will not get satisfaction or deep sleep.
- Toothache and decay: You will be surprised to know that 99% of calcium in our body is stored in teeth and bones. calcium is the main constituent to make our teeth so, any deficiency will affect the teeth adversely and may result in toothache and decay.
- Brittle and weak nails indicate calcium deficiency as calcium is essential for healthy and strong nails.
- Poor bone density is a serious concern of low calcium levels, especially in children. Calcium deficiency in children may lead to muscle-ache, easy fractures, spasms and in worst case -rickets.
- Apart from the above mentioned main symptoms people may also suffer from fatigue, late signs of puberty, frequent illness etc.
As mentioned earlier calcium needs vitamin D to be absorbed by the human body efficiently. There is no clear pattern for vitamin D deficiency. In fact, most of the people remain asymptomatic despite low levels.
Causes of Vitamin D Deficiency
Insufficient exposure to sunlight and nutritional deficiency are the major cause of vitamin D deficiency.
There are other wide range of factors too that can affect the vitamin D absorption in your body such as disorders of the gut and pancreas, liver and kidney diseases etc.
Your age and skin colour will also decide on how efficiently your body converts sunlight to vitamin D. People with black skin need more sun exposure than the white skinned people to get adequate level of vitamin D.
As we age, our kidney’s ability to convert vitamin D to its active form reduces. People with obesity (body mass index of 30 or greater) are often low in vitamin D blood levels.
When we talk about vitamin D deficiency due to lack of sun exposure, the surprising factor that has come out of various studies is that even after abundant availability of sunlight round the year, more than 70% Indian are deficient in vitamin D. Experts attribute it to
- Fast-paced and stressed-out lifestyles in India. More and more Indians are working longer hours with little or no time for outdoor activities (leading to sun exposure), more and more people are suffering from vitamin D deficiency.
- Increasing sun avoidance among youth to stay fairer and also with increasing usage of sunscreen.
- Increasing consumption of vitamin deficient junk food.
- Avoidance of Vitamin D carrying food products.
- Vegetarianism among Indians. Vitamin D is primarily found in the flesh of fatty fish (such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel) and fish liver oils are among the best sources. Small amounts of vitamin D are found in beef liver, cheese, and egg yolks.
Common Vitamin D Deficiency Diseases
Vitamin D deficiency has emerged as a major public health problem worldwide. Apart from making for a good healthy bone, Vitamin D has several other roles including neuromuscular and immune function, modulation of cell growth and reduction of inflammation. Many genes encoding proteins are also modulated by vitamin D. Almost every cell in our body has vitamin D receptors and hence the lack of vitamin D can severely affect our health.
The Complete Vitamin D Deficiency Diseases List
Vitamin D deficiency has become global epidemic. In India, this phenomenon is rampant as the potential benefits of plentiful sunlight throughout the year is majorly negated by traditional and cultural practices. Vitamin D deficiency has been shown to play a role in almost every major disease. These includes:
- Rickets in children,
- Inflammation,
- Influenza
- Osteoporosis and Osteopenia
- 17 varieties of Cancer (including breast, prostate and colon)
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Obesity
- Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes
- Autoimmune diseases
- Multiple sclerosis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Osteoarthritis
- Bursitis
- Gout
- Infertility and PMS
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Depression and Seasonal Affective Disorder
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Fibromyalgia
- Chronic Pain
- Periodontal disease
- Psoriasis
Diseases in Detail:
Chronic Kidney Disease
Vitamin D deficiency is very common among people with chronic kidney disease. Vitamin D is converted into its active form calcitriol by kidney and liver. Calcitriol is required for the intestines to absorb the calcium and phosphorus. Calcium and phosphorus, in turn, are crucial for building healthy bones.
People with chronic kidney disease are unable to convert the inactive form of vitamin D (D2 and D3) to its active form (Calcitriol) and hence suffer from weak bones, muscle spasms, stress fractures, rickets, osteomalacia etc.
Parathyroid Disease and Vitamin D
Parathyroid is a hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands (located in the neck area near the thyroid glands). During the kidney failure, parathyroid glands may get a wrong signal that there is not enough calcium in the bloodstream. Hence, to compensate the calcium level in bloodstream parathyroid glands generate more Parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH instruct our body to pull out the calcium from the bones and put them into bloodstream. PTH level sometimes may go out of range while trying to compensate the calcium level and hence cause secondary hyperparathyroidism. People with secondary hyperparathyroidism may suffer from bone pain and it also makes the bones weak that fracture easily.
Excess level of calcium in blood may result in reduction in blood flow, calcification in heart (resulting in heart attack), difficulty in breathing due to calcification in lungs, etc.
Vitamin D receptors found in healthy kidney, efficiently turns vitamin D into it active form. The active form of vitamin D controls the absorption of calcium and phosphorus (from food) and thus maintain the balance of these minerals in your body. It also helps in maintaining the PTH level in your body. In case of kidney failure, vitamin D is not converted into its active form which affects the balance of calcium and phosphorus. PTH tries to overcompensate and out of range. That’s the reason PTH level is checked every three months for the person having kidney problems.
Bone diseases caused by Vitamin D deficiency
As we already know vitamin D is essential for bone health and hence low level of vitamin D can surely have adverse effect on bones. Below are the main bone diseases caused due to vitamin D deficiency:
- Rickets
- Stress fracture
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoporosis
- Osteomalacia
Rickets and Vitamin D
Rickets is a childhood skeletal disorder which affects bone development in children. Due to rickets, the bones become soft and weak which may lead to bone deformities. It is a disease that is caused by deficiency of vitamin D or calcium or phosphorus.
In most of the cases, rickets occurs due to lack of vitamin D as our body needs vitamin D to absorb calcium efficiently from the intestines. So even if we intake calcium rich foods, it will not be absorbed by our body if we are low in vitamin D.There are two types of rickets:
- calcipenic (hypocalcemic) – rickets caused by calcium deficiency.
- phosphopenic (hypophosphatemic)- rickets caused by phosphate deficiency
Rickets in adults is known as osteomalacia (known as soft bones). Some common signs of rickets are:
- Delayed growth
- Muscle weakness
- Pain in the spine, legs and pelvis
- delayed formation of teeth
- short stature and poor weight gain
- Delayed walking
- fractures in severe cases
- Softening of the skull
Rickets causes the growth plates (at the ends of a children’s bones) to become soft and therefore the skeletal deformities take place such as bowed legs, knock knees, breastbone projection, etc. Children may also have some medical condition that adversely affect the vitamin D absorption by their bodies such as: Celiac disease, Cystic fibrosis, Kidney problems, Inflammatory bowel disease, etc.
Vitamin D resistant Rickets
Vitamin D resistant rickets (scientifically called Hypophosphatemic rickets) is a disorder in which ingestion of vitamin D become relatively ineffective. This condition arises due to low serum phosphate levels in the bloodstream. The symptoms usually begin from the first month of life and can range in severity. Skeletal deformities and abnormality of dental enamel are classic signs of Hypophosphatemic rickets.
Hypophosphatemic rickets is a result of mutation in the PHEX gene and often thought to be hereditary. Some of the genes associated with hereditary hypophosphatemic rickets, directly or indirectly regulate a specific protein that reduces phosphate re-absorption by the kidneys into bloodstream. Mutations affect the function of these genes which results in increased production (or reduced breakdown) of the protein. The overactive protein generated as a result of mutation reduces the kidney’s ability to reabsorb phosphate, leading to the symptoms of the condition.
Vitamin D and risk of Dementia and Alzheimer Disease
Various studies and meta-analysis have shown that the fat soluble, hormone vitamin D has many health-promoting effects and potential to combat many disorder, including the non-skeletal ones such as Alzheimer Disease (a form of dementia) and other cognitive impairments. There are many reports that suggest, vitamin D deficiency may cause or increase the risk of AD or dementia as the patient of AD and dementia have been found to have low levels of vitamin D in their blood. These all point towards the fact that increased intake of vitamin D can be a huge boost for people with cognitive impairments. There is no conclusive evidence but studies on many AD and dementia patient have made a statement that vitamin D has a big role in treating these ailments.
Vitamin D Deficiency Diseases in Children
Children, especially those who are completely dependent on breast milk are likely to fall under the vitamin D deficiency range. As indicated by research data across the world this phenomenon is rampant and have affected more than 65% of children worldwide. Here is the list of diseases caused due to lack of vitamin D in children:
- dental deformities
- impaired growth
- short stature
- skeletal deformities such as rickets.
Vitamin D and Breast Cancer
A new study that was conducted using cell lines and mice indicates an association of vitamin D levels with tumour growth and metastasis in many types of cancer (including breast cancer). The findings of the study were published on March 2 in Endocrinology. According to the study the breast cancer patient have low level of vitamin D while developing it.
One more research says, calcitriol (active form of vitamin D) binds to the vitamin D receptors in our body, which regulates a large number of genes. Some of these genes are also associated with cancer cells. Even though, it has not been proven scientifically, the significance of vitamin D in preventing the cancer cannot be ignored.
Vitamin D and Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer is a rare but an aggressive disease. As per the hypothesis established by University Medical Centre Utrecht (UMCU), vitamin D concentrations and dietary vitamin D intake are linked with subsequent pancreatic cancer risk. (5)
A certain study claims that worldwide, more than 75% of cancer patients (including patients of pancreatic cancer) have low levels of vitamin D. The study also suggests that people with lowest levels of vitamin D are more likely to be associated with more advanced cancers. However, the direction of the association between higher level of vitamin D and lower cancer incidence is still unclear, and calls for additional scientific research.
Vitamin D and Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is more common in areas with an inadequate amount of sun exposure. Data from various Research on human suggest that Lower levels of vitamin D are associated with more aggressive forms of prostate cancer. The research also states that men with lower vitamin D levels are more prone to death from prostate cancer or have it spread in other body parts.
Hair Loss due to Vitamin D deficiency
Directly or indirectly, Vitamin D has a lot to offer to the people suffering from hair loss. Keratinocyte is understood to be critical for the survival of the hair follicle and Vitamin D plays a vital role in the proliferation of keratinocytes. Thus, it’s very much evident that vitamin D deficiency will have an adverse effect on hair cycling.
In a study on genetic hair loss (androgenetic alopecia), 80 women (suffering from women pattern baldness) were found to have low levels of vitamin D and ferritin (a protein that enables cells to store iron). Study also concluded that proper supplementation could benefit people in case of genetic hair loss.
Vitamin D Deficiency Treatment
Surprisingly, among all the nutrient deficiency, vitamin D is the most under-diagnosed and under-treated in the world even after being a widespread phenomenon. Vitamin D is an essential vitamin for overall good health, strong bones, functioning of your muscles, brain, lungs & heart and ensures that your body is capable of fighting infection. Any level of deficiency of such an important nutrient should be noticed and treated before it develops into something incurable posing serious threat to one’s life.
Vitamin D Deficiency Treatment Guidelines
How to Increase Vitamin D Levels Quickly
Adults should take approx. 600 IU of vitamin D every day, while elder people can take 800 IU daily. Here are the ways to increase level of vitamin D in blood:
- Embrace the sunlight at least 20-30 twice a week (without sunscreen) and double the time during winter.
- Cod liver oil is considered the best oral source of vitamin D.
- If you are a non-vegetarian, try to add vitamin D rich foods in your diet such as fatty fish (salmon, tuna, shrimp, etc.).
- For vegetarian, some kind of mushrooms (exposed to UV rays) are excellent source of vitamin D and can spike the vitamin D level very quickly.
- Try to consume vitamin D fortified foods (milk, cereals, orange juice) as much as possible.
- A good vitamin D supplement can do the wonder too.
- There are couple of vitamin D co-factors such as Magnesium, vitamin A & K, zinc and boron. All these nutrients help human body absorb and use vitamin D efficiently. So, you also need to include food sources that are rich in these nutrients.
Homeopathic Medicine for Vitamin D Deficiency
Apart from natural sources and supplements there are some homeopathic treatment which could help you increase vitamin D level. Couple of remedies used in homeopathy to treat vitamin D deficiency are: Calc Carb biochemic, Arnica, Calc Phos biochemic, Rhus Tox, Acid Phos.
Cod Liver Oil Vitamin D Best Source
Among the natural vitamin D sources that can be consumed orally, cod liver oil is the best known source. You will be surprised to know; one table spoon of cod liver oil provides 1360 IUs (International Units) which is 340% of daily recommended intake. Next time when you fall prey to low vitamin D level; consider having a sip of cod liver oil as it can boost your vitamin D level in no time.
Sun & the Vitamin D Connection
People who think Vitamin D is called sunshine vitamin for no reason are the ones fooling themselves for no reason. Almost 95% of vitamin D that our body needs come from sunlight. No way you can ignore the importance of mighty sun and if you do so God bless you!
According to a report vitamin D is more prevalent in those regions which are not privileged with enough sunlight round the year. This fact speaks for itself.
How to get Vitamin D from Sun
It’s not a nuclear science to know how to get vitamin D from sun, is it? You just need to stroll out in a sunny day for 20-30 minutes or bit more if it’s the winter season and you are done. No wait! There are other factors that may hamper the amount of vitamin D such as sunscreen, cloudy weather, pollution, your skin type and the list goes on. But why to blame sun for that? He is definitely not the culprit here. As far as sun is concerned you got to get out of your house and try to be as less covered as possible, rest of the factor should be taken separately.
Vitamin D Sun Exposure Chart
| Sun Exposure Chart for Different Skin Types and UV Index | |||||
| Skin Type | UV: 0-2 | UV: 3-5 | UV: 6-7 | UV: 8-10 | UV: 11+ |
| Always burn, never tan | 0 minutes | 10-15 mins | 5-10 mins | 2-5 mins | 1-2 mins |
| Easily burn, rarely tan | 0 minutes | 15-20 mins | 10-15 mins | 5-10 mins | 2-5 mins |
| occasionaly burn, slowly tan | 0 minutes | 20-30 mins | 15-20 mins | 10-15 mins | 5-10 mins |
| Rarely burn, rapidly tan | 0 minutes | 30-40 mins | 20-30 mins | 15-20 mins | 10-15 mins |
| Never burn, always dark | 0 minutes | 40-60 mins | 30-40 mins | 20-30 mins | 15-20 mins |
Best Time to get Vitamin D from Sun in India
Well it depends on the season you are talking about. India has many seasons but let us just concentrate on winter and summer. In summer 9-11 am is the best time to get vitamin D, later on you may be prone to sun burn, after all India is hot, isn’t it? During winter the best time to get sun bath is between 11am to 3 pm. Usually evening time is not considered good to get vitamin D, so avoid doing so. Some people say, irrespective of the season, best time to get vitamin D is when your shadow is shortest. Well, people are entitled to their opinion we recommend what we have aforementioned.
References:
- Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] Concentrations and Health. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/#en1
- The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (AJCN) http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/early/2014/03/12/ajcn.113.073734.abstract
- Vitamin D and the Immune System, Cynthia Aranow, MD, Investigator, NCBI. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3166406/
- 5 Signs You’re Not Getting Enough Vitamin D, By Karla Walsh, Prevention http://www.prevention.com/health/symptoms-of-vitamin-d-deficiency/slide/3
- Vitamin D and pancreatic cancer risk. World cancer reserach fund international. http://www.wcrf.org/int/research-we-fund/what-we-re-funding/vitamin-d-and-pancreatic-cancer-risk