Thyroid Gland needs sufficient amount of Iodine on a daily basis through diet for its proper functioning. Lack of Dietary Iodine may lead to malfunctioning & enlargement of Thyroid Gland tissues and cause the Goitre Disease. Iodine content in the body is 20 to 30 mg. Out of this Iodine body content 8 mg is found in the thyroid gland.
Iodine deficiency has become one of the most common problem worldwide. The major cause of iodine deficiency is inadequate intake due to low soil concentration, with resulting low concentration in crops. The iodine content of plants grown in iodine-deficient soil may be as low as 10 micro-gram/kg, compared with 1,000 micro-gram/kg for plants grown on soils with high iodine content.
Contents
What is Thyroid Gland
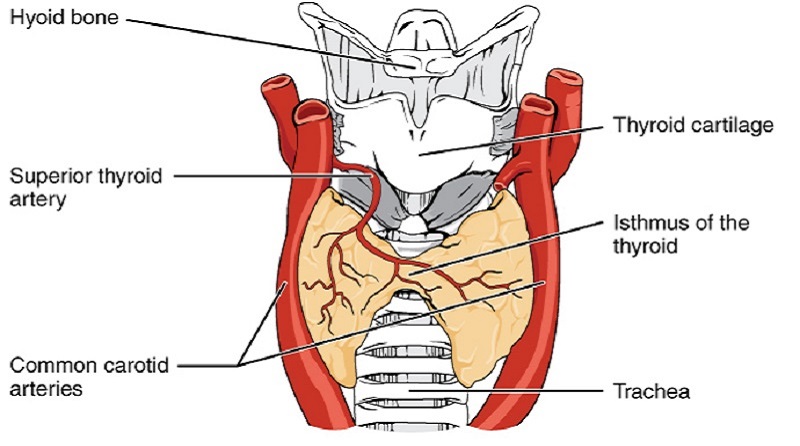
Thyroid Gland is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body. Thyroid Gland is of the shape of a butterfly and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple).
Just like other endocrine organs Thyroid Glands secrete hormones directly into the circulatory system. Thyroid Gland is responsible for secretion of following Hormones:
Hormones Secreted by Thyroid Gland
| Secreted hormone | Abbreviation | From cells | Effect |
| TriIodothyronine | T3 | Thyroid Epithelial cell | Active form of Thyroid Hormone. T3 stimulates body oxygen and energy consumption, thereby increasing the basal metabolic rate. It Stimulates RNA polymerase I and II, thereby promoting protein synthesis. |
| Thyroxine (Tetra-Iodothyronine) |
T4 | Thyroid epithelial cells | Less active form of thyroid hormone. T4 is a precursor of T3. |
| Calcitonin | Parafollicular cells | Stimulates osteoblasts and thus bone construction. It Inhibits Ca2+ release from bone, thereby reducing blood Ca2+ |
The Thyroid hormones primarily T3 and its precursor T4 are Tyrosine (an Essential Amino Acid) based hormones produced by the thyroid gland. T3 and to a lesser extent T4 are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism.
Thyroid Gland & Iodine’s Significance in Production of T4 & T3 Hormones
Iodine (I) is necessary to make thyroid hormone, a regulator of energy metabolism that is vital for normal growth and development, maintenance of body temperature, and brain development. Thyroxine (T4) contains 4 iodine atoms and trilodothyronine (T3) contains 3 iodine atoms, so iodine constitutes 65% and 59% of T4 and T3, respectively. Dietary organic iodine is converted to iodide in the gut and absorbed throughout the gastrointestinal tract. Needless to say that a deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4. Deficiency of Iodine could enlarge the Thyroid Gland tissues and cause the Goitre Disease.
The Thyroid hormones are essential for:
- Proper development and differentiation of all cells of the human body
- Regulation of protein, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism
- Human cells use of energetic compounds
- Stimulation of vitamin metabolism
- Numerous physiological and pathological stimuli that influences thyroid hormone synthesis
- Heat generation in humans
Health concerns due to Iodine deficiency
Iodine deficiency is known to affect all stages of life.
Impact of Iodine Deficiency on the fetus
It can lead to abortions, stillbirth, congenital anomalies, increased perinatal mortality, endemic cretinism and deaf mutism.
Impact of Iodine Deficiency on the neonate
It can cause goiter, hypothyroidism, mental retardation and increased susceptibility of the thyroid gland to nuclear radiation. Neonatal screening can prevent neurological consequences of congenital hypothyroidism in infants after birth.
Impact of Iodine Deficiency on Children and Adolescent
In children and adolescents, iodine deficiency can lead to goiter, subclinical hypothyroidism, subclinical hyperthyroidism, impaired mental function, retarded physical development and susceptibility of the thyroid gland to nuclear radiation.
Impact of Iodine Deficiency on Adults
Finally, in the adult, the consequences of iodine deficiency are goiter, hypothyroidism, impaired mental function, spontaneous hyperthyroidism in the elderly, iodine-induced hyperthyroidism and Increased vulnerability of the thyroid gland to nuclear radiation. Iodine deficiency coupled with high goitrogen intake for a long time period can bring about goiter.’ The combination of goitrogenic thiocyanides with selenium deficiency is a risk factor for endemic myxedematous cretinism. Iodine deficiencies are the leading cause of preventable mental retardation worldwide.
Thyroid Gland and Iodine Mineral Supplement
From the above it is very clear that Supplementation of Iodine mineral is extremely critical for a healthy and fulfilled life. The best or most Bio-Available or Active form of Iodine Supplement in India are Potassium Iodide and elemental or nascent Iodine.