Vitamin C or L-ascorbic aThe cold season is approaching, and with it comes the usual attack of sniffles, coughs, and tiredness. The most intelligent thing to do before the flu strikes is to boost your immunity, and that is where Vitamin C comes in. Vitamin C is recognized to have strong immune-boosting powers and can help your body fight infections and recover more quickly.
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid, or simply ascorbate, is an essential nutrient for humans. It is a water-soluble vitamin that is necessary for normal growth and development.
Vitamin C is not merely a buzzword for citrus fruits. It is critical to keep your body healthy on a daily basis, whether improving immunity or healing tissues. However, not everyone is aware of all the facts regarding vitamin C – its lesser-known roles, safe doses, or natural sources.cid, or simply ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans. It is a water-soluble vitamin that is necessary for normal growth and development.
We have provided evidence-based facts that you hardly ever got to know in school. We also cover the significance of vitamin C, its purpose, the effects of excess vitamin C, and its natural sources.
Continue reading to understand further the vitamin C benefits, its colours, the source of vitamin C, and the wisdom of using vitamin C.Check out this detailed blog on VitsuppVitamin C Tablets to learn how they enhance general immunity and health.
Surprising Vitamin C facts

We can only think of oranges when we hear about it. However, there is much more to such a potent nutrient. The facts may surprise you regarding the unknowingly present role of Vitamin C in sustaining youthful skin, as well as in unexpected food items that contain more Vitamin C than citrus fruits.
Do you think you know everything about vitamin C? Well, let’s find out how much.
1. Humans cannot produce Vitamin C, but dogs can
Humans, unlike most other animals, do not have an enzyme (L-gulonolactone oxidase) necessary to make ascorbic acid, also known as Vitamin C. It implies that we need to consume it daily, either through fruits, vegetables, or supplements, to maintain our health.
2. Ascorbic Acid – The Fancy Name for Vitamin C
The quantity of vitamin C you can store in your body is minimal, which means that you should either get it in food or supplements, or get it from nature. In scientific terminology, vitamin C is referred to as L-ascorbic acid, L-ascorbate, or ascorbate in its salt form.
3. Vitamin C – in different forms
Vitamin C exists in different forms. The most prevalent forms in terms of foods or supplements consist of ascorbic acid or sodium ascorbate and calcium ascorbate. The pure ascorbic acid is acidic and is in the form of white or light yellow. Nevertheless, the commercial preparations, either as a tablet or as a powder, may include added colourings or coatings which alter the colour of vitamin C to yellow or orange.
4. The safest supplement you can take
The body absorbs it and excretes the unwanted amount of it via urine as a result of its water solubility.
This characteristic prevents poisoning on regular consumption. Unlike other fat-soluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K, excess vitamin C is not a serious issue. Nonetheless, even consuming large quantities of supplements may result in side effects, as we will see later.
5. Vitamin C – A Healer
Vitamin C is needed for the growth and repair of tissues in all parts of your body. It is used to:
It forms an important protein used to make skin, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels. This vitamin heals wounds and forms scar tissue. It also repairs and maintains cartilage, bones, and teeth.
One of its most unique functions is that it is a cofactor of enzymes that are involved in the production of collagen, the structural protein found in the skin, tendons, cartilage, blood vessels, and bones.
6. Sound mental health
Many researchers have now linked Autism to heavy metal toxicity. According to Dr. Amy Yasko, regular intake of therapeutic levels of vitamin C alone may help some individuals detoxify the heavy metals.
7. The finest antioxidant
Vitamin C is an antioxidant. Antioxidants are nutrients that can block some of the damage caused by free radicals. Free radicals are made when your body breaks down food or when you are exposed to tobacco smoke or radiation. The buildup of free radicals over time is largely responsible for the aging process. Free radicals may play a role in cancer, heart disease, and conditions like arthritis.
The best food sources of vitamin C are uncooked or raw fruits and vegetables. All fruits and vegetables contain some amount of vitamin C.

To learn the importance of vitamin C, you need to know about how many processes in the body require it. Vitamin C is a potent antioxidant. It deactivates free radicals (unstable molecules), thereby restricting oxidative stress and preserving the cells.
This antioxidant activity is the foundation of most of its vitamin C advantages.
The following are some of the major advantages and the science behind them:
8. How Vitamin C Powers Up Your Immunity
Vitamin C stimulates the immune response of body cells, increasing the efficacy of white blood cells, adding to the barrier effect, and potentially reducing and lightening the duration and severity of infections.
However, its effect on general cold prevention is not very high, but it may have a small impact on the reduction of the duration of symptoms.
9. Boost Iron Absorption with Vitamin C
In individuals consuming plant-based foods, vitamin C improves absorption by transforming iron into an easier form to be absorbed by the bowel.
The benefit can be used to prevent iron deficiency or anemia among the risk groups.
10. Vitamin for A Healthy heart
Various research studies indicate that vitamin C might have a small effect in lowering blood pressure and enhancing blood vessel functioning.
It is also capable of reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol as well as triglycerides, but the evidence is inconclusive.
11. Protects against chronic disease risk
Vitamin C may be beneficial in preventing chronic diseases, such as heart disease, certain types of cancer, and cataracts, due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties; however, clinical trials are inconclusive.
Put simply, vitamin C has a wide range of effects, including enhancing immunity, promoting tissue repair, regulating iron metabolism, and protecting cells. Since your body fails to store it, you must take it regularly, either through a balanced diet or supplementation (if safe). Next, we will discuss the natural sources of vitamin C and their sources in the following section.
12. These Fruits Pack More Vitamin C Than Oranges
When discussing vitamin C in its natural form, we can refer to fruits as the primary and most ideal sources. They are highly nutritious, bioavailable, and contain other essential nutrients, including fiber and antioxidants. Some of the fruits that are the best sources of vitamin C, and their importance, are listed below.

Cantaloupe
Cantaloupe is a refreshing summer fruit that is rich in water and electrolytes. The 1 cup contains nearly fifty percent of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C. It also contains a significant amount of beta-carotene, which supports eye health maintenance.
Citrus fruits and juices, such as orange and grapefruit
Oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruits are the most common sources of vitamin C. An average orange contains nearly 70mg of vitamin C, and a portion of grapefruit provides the same. They are easy to drink in fresh form, and whole fruits also contain fiber.
Kiwi fruit
Kiwi is not a well-known fruit, but it is worth noting that a Kiwi has more vitamin C than an orange. A single kiwi fruit will provide around 70mg of vitamin C, vitamin K, potassium, and fiber.
Mango
Mango is a very good source of vitamin C and also vitamin A, which makes the skin healthy.
Papaya
Papaya is another fruit that is rich in vitamin C. Each cup of papaya cubes has a content of more than 85mg that enhances digestion, skin, and calms inflammation.
Pineapple
Pineapple is also a source of vitamin C and bromelain, a digestive and anti-inflammatory enzyme.
Berries such as strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, and cranberries
Strawberries, raspberries, blueberries, and cranberries are examples of berries that contain vitamin C. Vitamin C is especially abundant in strawberries, where the amount of vitamin C in a cup is around 89mg.
Watermelon
Lastly, watermelon is a healthy source of hydration and a cooling source of vitamin C, albeit in lesser quantities than citrus and kiwi.
Explore more healthy options beyond fruits with our guide to the 41 Most Nutritious Fruits and Vegetables on Earth
13. Vegetables You Never Knew Were Super Sources
When talking about sources of Vitamin C, we commonly think about Fruits. Nevertheless, there are many vegetables that are also excellent sources of this essential nutrient. Indeed, certain vegetables have even more vitamin C than the common citrus fruits. Besides supplementing your vitamin C levels, it is also important to add them to your daily meals to get extra fiber, minerals, and antioxidants that provide health-promoting effects.

Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cauliflower
Broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cauliflower belong to the Cruciferous family, and they contain vitamin C. A single cup of cooked broccoli will contain close to 80mg of vitamin C, and Brussels sprouts (especially when lightly cooked) can supply more than 70mg/cup of vitamin C, vitamin K, and folate. Cauliflower is also a good source of vitamin C, and it contains very few calories.
Green and red peppers:
Green and red peppers are also among the best sources of vegetable vitamin C. Half a cup of the raw red bell pepper has around 95 mg, beating the medium orange. Green peppers are cheaper, though full of vitamin C and other antioxidants, including beta carotene.
Spinach, cabbage, turnip greens, and other leafy greens
Spinach, cabbage, turnip greens, and other leafy greens also contain vitamin C in high amounts. They contain a lesser amount of nutrients than peppers, but contain other vitamins and minerals like iron, magnesium, and vitamin A. The absorption of iron may be enhanced by eating leafy greens along with foods that have vitamin C.
Sweet and white potatoes
White and sweet potatoes are not commonly known but are also good sources of vitamin C. They are also sources of potassium and fiber in addition to vitamin C, albeit not as high as peppers. Sweet potatoes also contain beta-carotene, which keeps the eyes and skin healthy.
Tomatoes and tomato juice
Tomatoes and tomato juice can also be used to supplement your vitamin C intake. Average medium tomatoes will contain around 20 mg of vitamin C in a tomato, but tomato juice may have over 30 mg in a cup.
Winter squash
Winter squash is a great alternative to other foods rich in vitamin C, fiber and antioxidants, and hence it is an ideal complement to hearty meals.
14. Warning Signs Your Body is Starving for Vitamin C
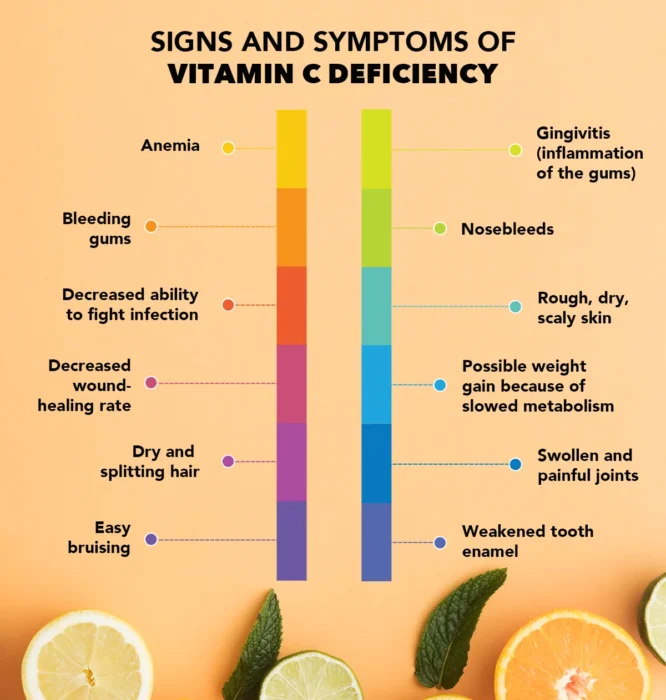
Anaemia and deteriorating gum health
Vitamin C plays a significant role in physical health, and its deficiency may lead to certain symptoms that are easy to detect. One of the early manifestations is anaemia because vitamin C boosts the absorption of iron in food. Vitamin C deficiency can also render the body incapable of sustaining healthy levels of red blood cells. There is also a high likelihood of bleeding gums, gingivitis, and frequent nosebleeds because this nutrient is important in keeping the blood vessels and the gum tissues strong.
Weakened immunity
The lack of vitamin C weakens the immune system, resulting in an inability to fight infections and slow wound healing successfully. The hair becomes dry and develops split ends, and the skin is generally rough, dry, and scaly. Easy bruising and painful, swollen, and tender joints may also develop in the patient, as vitamin C plays a pivotal role in collagen synthesis, which keeps the connective tissues, cartilage, and skin elastic.
Other symptoms
Other symptoms include weakened tooth enamel, which makes the teeth more prone to decay, and a lack of reason as to why a person gains weight, since in some cases, their metabolism. Scurvy is a long-term and acute deficiency that has been known to afflict seamen on long voyages. Extreme fatigue, agonizing pains in joints, gum diseases, and slow healing even of small wounds are some of the symptoms of scurvy.
Stay strong, stay healthy. Explore Vitamin C Tablets and our Oral Care range to complete your wellness journey.
15. Risk groups
Indeed, some groups are more vulnerable to deficiency. The smokers and secondhand smokers should consume more vitamin C, as the chemicals in cigarette smoke deplete it. Similarly, pregnant and breastfeeding mothers require increased amounts to ensure their own health and that of their infants. The elderly are also vulnerable, especially those who consume unhealthy food.
Complications can be prevented through the early detection of these warning signs and the consumption of vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits, berries, peppers, and leafy greens, to help restore normal health.
Hence, here are the lists of symptoms arising from vitamin C deficiency –
- Anemia
- Bleeding gums
- Decreased ability to fight infection
- Decreased wound-healing rate
- Dry and splitting hair
- Easy bruising
- Gingivitis (inflammation of the gums)
- Nosebleeds
- Possible weight gain because of slowed metabolism
- Rough, dry, scaly skin
- Swollen and painful joints
- Weakened tooth enamel
16. Vitamin C Excess: Can Too Much Vitamin C Hurt You?

Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin, which means the body does not store it. Instead, the excess is usually filtered out through the urine, which makes severe side effects rare. However, an excessive dose (over 2,000 mg per day) is not always recommended since it may produce some undesirable effects.
One of the most common side effects of overconsumption is stomach upset that includes bloating, cramps, and nausea. Vitamin C is acidic as well, and therefore, it can cause heartburn or exacerbate acid reflux in sensitive patients. The other prevalent issue is diarrhea, which is an outcome of the digestive system attempting to eliminate the unabsorbed vitamin as soon as possible.
High doses may also result in the formation of kidney stones to a very high extent, especially to those who are prone to the disease. The reason is that extreme levels of vitamin C may be broken down to oxalates that may build up to cause the formation of stones. Additionally, there is also the possibility of excessive supplementation, which disturbs the absorption of other vitamins such as vitamin B12 and copper.
Most people need no more than a healthy diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables and is not in danger of overdose of vitamin C. The supplements should be taken in moderatio,n and it is always desirable to follow the recommended daily allowance.
17. How Much Vitamin C Do You Really Need?
The daily consumption of vitamin C depends on age, gender, and lifestyle. The recommended dosage, as per the Mayo Clinic, in healthy adults ranges between 65 and 90 milligrams per day, with a maximum safe dose of 2,000 milligrams per day.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women need a bit more to meet the requirements of maternal and infant health. Smokers also require approximately 35 milligrams daily over that of non-smokers because tobacco smoke triggers oxidative stress and depletes vitamin C.
The most effective and safest way of meeting these demands is by consuming a balanced diet of fruits and vegetables.
Learn how to pick safe doses by reading 10 Tips to Help You Choose the Best Supplement
Conclusion
Vitamin C is not only a common nutrient, but it is also an essential constituent of health and well-being. This potent antioxidant is involved in nearly all bodily functions, including supporting immunity and collagen production, as well as defense against oxidative stress. Most people do not need a supplement, as a balanced diet comprising fruits, vegetables, citrus fruits, berries, broccoli, and leafy greens provides sufficient amounts of the required nutrients.
Nevertheless, it is also crucial to learn about the risks of deficiency as well as the consequences of overconsumption. Although deficiency may result in fatigue, poor immunity, and, in rare cases, scurvy, over-supplementation may cause stomach discomfort and, in extreme cases, kidney stones. Balance is the key: by taking the recommended daily intake, one is bound to experience maximum benefits without any side effects.
With the hectic lives we lead in the modern world, where our immune systems are constantly put to the test by stress, pollution, and processed foods, a sufficient supply of vitamin C is now more important than ever. Regardless of whether it is fresh produce or supplements (as required), maintaining healthy levels can increase energy, improve skin health, and enhance natural defenses. Vitamin C is, in short, a simple but effective method of protecting long-term health.
FAQ/Top FAQs About Vitamin C Answered:
One interesting fact about vitamin C is that the human body cannot produce or store it. We have to obtain it daily through food or supplements, unlike certain animals. Another name of Vitamin C is ascorbic acid. It is also crucial in the production of collagen, wound healing, and immunity. It is also a powerful antioxidant, which helps prevent damage to cells caused by free radicals. Such vitamin C sources include citrus fruits, berries, and vegetables, such as broccoli. This demonstrates its significance in day-to-day health. Deficiency symptoms may manifest within a short time if intake is irregular.
To determine whether the vitamin C is authentic or not, you can look for the name ascorbic acid on the label, which is its scientific name. Pure vitamin C supplements are typically available in the form of a crystalline, white powder. Vitamin C does not show its color in naturally occurring foods like fruit and vegetables, but the nutrient is contained within. Another method to verify authenticity is by purchasing from renowned brands. If it is easily dissolved in water and has a slightly tart taste, it is likely to be real vitamin C, which can be verified by reading third-party certifications and ingredient lists. It would be best to always buy from trusted sources.
Vitamin C is made of water-soluble ascorbic acid, which is the real vitamin C. It can exist in the forms of pure ascorbic acid in supplements or mixed with minerals, such as calcium or sodium, to create mineral ascorbates. These are less burdensome on the stomach. Of course, citrus fruits, berries, peppers, tomatoes, and leafy greens contain vitamin C. Natural and synthetic vitamin C have identical chemical structures and functions. They both offer the same benefits to the body, including improved immunity, enhanced collagen production, and increased iron absorption. Thus, both natural and artificial sources are considered real sources of vitamin C.
In most instances, the kiwi fruit has the highest content of vitamin C, but guava is even better. One guava can provide over twice the amount of vitamin C required each day. Other sources, such as oranges, strawberries, papaya, and pineapple, are also rich in these nutrients. Oranges are the most popular of citrus fruits, but guavas have a higher quantity of vitamin C per serving. This demonstrates the importance of consuming a variety of fruits. They not only have vitamin C but also other vitamins and minerals. When you are picking fruits, it is best to pick colorful fruits, and this way, you are guaranteed to achieve the recommended daily intake.
Vitamin C is best absorbed in the morning, together with food. Your body absorbs it more effectively when it is taken in conjunction with a snack or meal, as it is water-soluble. Early intake can help reduce the risk of mild stomach upsets. Some individuals divide their dosage into two smaller doses, one in the morning and one in the evening, to enhance absorption. Vitamin C is also used to enhance the absorption of iron; therefore, it is beneficial to use it alongside a meal that contains iron. Nevertheless, avoid taking high doses at night, as it can cause stomach upset. It is not the time but the consistency of daily intake.
Vitamin C deficiency is manifested in various symptoms. The symptoms are frequent infections, weakness, and fatigue. Individuals can also observe swollen gums, bleeding gums, or slow healing of wounds. Dry skin and roughness, as well as dry, splitting hair, are also warning signs. Long-term deficiency usually presents itself in the form of easy bruising and painful, swollen joints. Severe cases result in the development of scurvy, characterized by anemia, gum disease, and impaired healing. There is an increased risk for smokers and individuals who have poor diets. It is important to identify these signs at an early stage. A deficiency can be reversed by obtaining vitamin C naturally through fruits and vegetables.
In the early 1930s, Hungarian scientist Albert Szent-Gyorgi discovered vitamin C. He separated it from paprika peppers and eventually found it to be the substance that prevents scurvy. He called it ascorbic acid, which prevents scurvy. This marked a breakthrough in the field of nutrition science. It explained why citrus cured the sailors of scurvy during extended ocean voyages. In this work, Szent-Gyorgi was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1937. His work emphasized the importance of vitamin C in terms of immunity, skin health, and overall well-being. His discovery holds great significance for human health today.
References:
- Escott-Stump S, ed. Nutrition and Diagnosis-Related Care. 6th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2008.
- Sarubin Fragaakis A, Thomson C. The Health Professional’s Guide to Popular Dietary Supplements. 3rd ed. Chicago, Il: American Dietetic Association; 2007.
- Institute of Medicine. Food and Nutrition Board. Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C, Vitamin E, Selenium, and Carotenoids. National Academy Press, Washington, DC, 2000.
- Douglas RM, Hemila H, Chalker E, Treacy B. Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold. Cochrane Database Syst Rev; 2007(3):CD000980.
- Naidu, K.A. (2003) Vitamin C in human health and disease is still a mystery? an overview – nutrition journal, BioMed Central. Available at: https://nutritionj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1475-2891-2-7 (Accessed: 08 October 2025).
- NIH , N. (no date) Office of dietary supplements – vitamin C, NIH Office of Dietary Supplements. Available at: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-HealthProfessional/ (Accessed: 08 October 2025).
- Julson, E. (2023) 15 signs and symptoms of vitamin C deficiency, Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-c-deficiency-symptoms#TOC_TITLE_HDR_16 (Accessed: 08 October 2025).
- Raman, R. (2025) 7 impressive benefits of vitamin C supplements, Healthline. Available at: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-c-benefits#prevents-gout (Accessed: 08 October 2025).



