If you are reading this article, I guess one of your loved ones is recently diagnosed with Autism or Autism Spectrum Disorder. What is Autism Spectrum Disorder? What is Autism meaning for a child and parents? If some of these questions are on your mind, we will help answering them in this blog post.
Contents
- What is Autism
- Autism meaning for a child and a parent
- Mental Retardation vs Autism
- Developmental delay with Autism
- Autism Symptoms, Behaviors, and Conditions
- What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
- Types of Autism or Classification of ASD as per DSM-V
- We are still learning about Autism
- Autism may not be genetic in Nature
- A good news for parents of children with Autism
- Get ready to recover his life
- Sources
What is Autism
Autism is an early developmental disorder, generally diagnosed in a child in the age group of 6 months to 3 years. In short it is a neuro-developmental disorder characterized by :
- Impaired Social Interaction
- Impaired Verbal and non-verbal communication
- Restricted and repetitive behavior.


Autism is an epidemic in India and the world today, however its awareness is abysmally low. Parents of Children with Autism are hesitant to talk about it, due to several actual and perceived notions. It is being reported off late that current incidence of autism is 1 in 68 children.
Autism meaning for a child and a parent
Autism is an early development disorder, in which the normal development of a child does not take place or gets delayed.
However, please note that children with Autism reach some of their developmental milestones at a normal pace and then regress. This generally happens in the first two years of a child’s life. The sign of autism develops gradually and become apparent before age three.

For a parent and a child following is the Autism meaning:
- It is a mental condition that is present from early childhood, however, may become apparent in first 2-3 years of life
- Generally characterised by great difficulty in communication
- Marked by difficulty in forming relationships with other people
- Visible in a child’s difficulty in picking up a language
- Visible in a child trouble understanding abstract concepts.
- It is considered to be a lifelong developmental disability. However, a child may recover from Autism fully with certain interventions.
- Autism is a spectrum condition. What it means is that not all children with Autism exhibit the same types and levels of difficulties. Autism will affect them in different and unique ways.
- A child with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) may communicate, interact, behave, and even learn in ways that are different from other people.
Mental Retardation vs Autism
Lot of individuals think that Mental retardation and autism is the same thing. However, please note that this is a misconception. They have nothing to do with each other. Autism is not a mental retardation, even if you feel people with autism behave like people with mental retardation.
To understand further let us learn the definition of Intellectual Disability, a new term that has replaced the word Mental retardation.
Intellectual Disability or Mental retardation is condition that includes the presence of the three below mentioned criteria:
- Significantly reduced ability to understand new or complex information, or to learn new skills. This is defined by Lower intellectual ability (usually an IQ of less than 70).
- Impaired intelligence with a reduced ability to cope independently (impaired social or adaptive functioning).
- Which started before adulthood, with a lasting effect on development through the life.
If you compare this with the definition of Autism above, you will notice that the key difference among the people with Autism and mental retardation is their learning abilities. Children with Autism are very intelligent, however children with mental retardation lack the necessary skills for daily living and have below-average intellectual capability.
Unlike children with Learning Disabilities (Mental Retardation), a child with Autism can have normal or above normal cognitive intelligence.
Developmental delay with Autism
Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASD), is also known as Pervasive Developmental Disorder (PDD) as it involves delay in many areas of development. The key developmental delays are with regards to social and verbal interactions. However you should be watchful of the following milestones. If you child is not achieving them, please connect with your practitioner.
- 6 months – Your child should have big smiles or other warm, joyful expressions.
- 9 months – Your child should start back-and-forth sharing of sounds, smiles, or other facial expressions with you.
- 11-12 months – Your child should start responding to their names, when called.
- 12 months – Your child should start babbling.
- 12 months – Your child should start interaction with you through non-verbal methods such as pointing, showing, reaching, or waving.
- 16 months – Your child should start speaking meaningful words.
- 24 months – Your child should start meaningful two word phrases that don’t involve imitating or repeating.
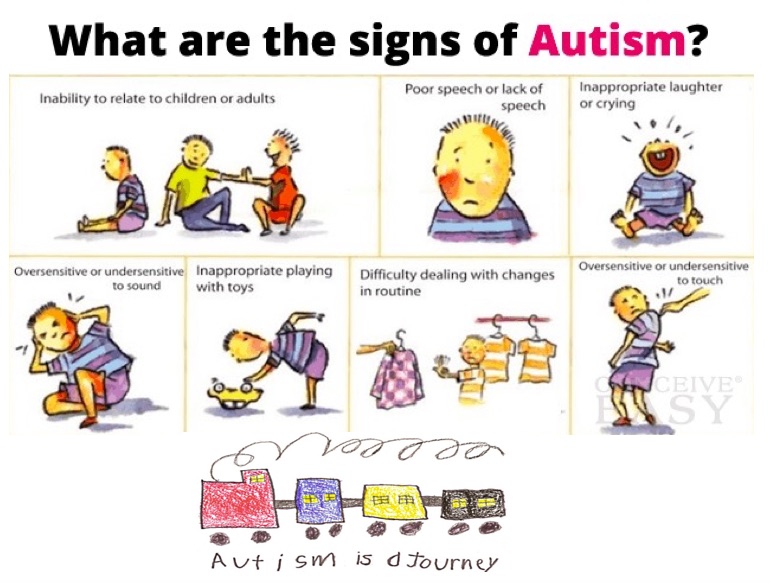
Autism Symptoms, Behaviors, and Conditions
Like no two individuals are same, similarly two people diagnosed with autism are also not same. They exhibit different symptoms, behaviours, conditions and the severity of all of these could vary. Below is the list of symptoms, behaviours and conditions presented by a child with autism:
- Anxiety
- Attention deficit
- Hyperactivity
- Hypersensitivity to
- Sound
- Light
- Touch
- Certain foods
- Environmental toxins
- Vaccines
- Hypersensitivity or impervious to pain, seeming lack of awareness of danger
- Impulsivity
- Self-stimulating behavior (stimming) such as rocking or twirling, hand flapping and other repetitive movements, rhythmic rocking
- Walking on tiptoe
- Severe language deficits
- Impaired social interaction & communication
- Loud, monotone voice
- Lack of use of the pronoun ‘I,’
- Referring to self in the third person echolalia (repeating others’ words or phrases)
- Prosody (sirigsong speech)
- Abnormal nystagmus (eye movement)
- Islets of ability (perfect pitch, unusual drawing or musical talent, calculation or rote memory skills, etc.)
- Preoccupation with light switches or other objects, spinning objects
- Repetitive, unusual and intense interests
- Repetitive acts and thoughts (stereotypes, mannerisms, perseverations, obsessions, and compulsions) using someone’s hand or arm as a tool, as if it is not attached to a human being.
- Absence of pointing
- Lack of shared attention (showing or pointing to something)
- No playing peek-a-boo
- Impaired nonverbal behaviors (eye contact, etc.)
- Incomprehension of gesture
- Seeming lack of interest in people
- Seeming unresponsiveness to verbal cues (parents may suspect deafness, but hearing tests normal)
- Blank remoteness
- Seemingly expressionless face resistance to change
- Tantrums or odd behavior in reaction to sudden change or for no apparent reason
- Laughing, crying, or showing other emotion for no apparent reason
- Lack of spontaneity
- Lack of curiosity
- Poor appetite
- Allergies
- Inability to process casein and gluten
- Fungal overgrowth
- Digestive problems
- Leaky gut syndrome
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Autoimmune problems
- Weakened immunity
- Chronic or frequent colds, flu, and ear and other infections
- Heavy metal toxicity
- Abnormalities in the brains of people with autism, variously in the cerebellum, limbic system, frontal cortex, and amygdala, and in brain waves.
- Elevated blood levels of the neurotransmitter serotonin in autistic people, but reduced uptake in the brain may mean that the availability of this vital nerve messenger is actually limited.
Here is a PDF from Help Autism Now, which will be a great resource for you.

What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
People use Autism and Autism Spectrum Disorder interchangeably today. However, Autism spectrum disorder or autistic spectrum describes a range of conditions classified as neuro-developmental disorders in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) as published in 2013.
The DSM-5 encompass the conditions prescribed for diagnoses of autism, Asperger syndrome, pervasive developmental disorder not otherwise specified (PDD-NOS), and childhood dis-integrative disorder.

What it means is that Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a group of developmental disabilities that can cause significant social, communication and behavioural challenges.
The learning, thinking, and problem-solving abilities of people with ASD can range from gifted to severely challenged. Therefore such people are referred to be on spectrum. Some people with ASD need a lot of help in their daily lives while others need less.
Features of these disorders include social deficits and communication difficulties, stereotyped or repetitive behaviours and interests, sensory issues, and in some cases, cognitive delays.
Types of Autism or Classification of ASD as per DSM-V
Autism
Autism forms the core of the autism spectrum disorders.
Asperger syndrome
Asperger’s Syndrome is also called High-Functioning Autism. Child with with Asperger syndrome have normal intelligence and language development but with several other traits seen in Autism. Child with Asperger’s Syndrome have difficulty with social skills, sensory inputs, making transitions and may need rigid routines. Their interests can focus on one area to the point that it is like an obsession.
PDD-NOS
PDD-NOS is diagnosed when the criteria are not met for a more specific autism disorder. It is also known as atypical autism or mild autism. What it means is that a child has developmental delays similar to Autism, however its intensity is much milder. A child with PDD-NOS does not meet the criteria for any other specific PDD/ASD.
Rett Syndrome(3)
Rett syndrome is a unique postnatal neurological disorder that is first recognized in infancy and seen almost always in girls, but can be rarely seen in boys. It occurs in 1 of every 10,000 girls world over.
Rett syndrome is not a degenerative disorder and causes problems in brain function that are responsible for cognitive, sensory, emotional, motor and autonomic function. These can include learning, speech, sensory sensations, mood, movement, breathing, cardiac function, and even chewing, swallowing, and digestion.
Childhood disintegrative disorder
Childhood disintegrative disorder is a condition in which children develop normally through age 3 or 4. Then, over a few months, they lose language, motor, social, and other skills that they already learned.
We are still learning about Autism
Our understanding of Autism has been evolving over the decades. In the beginning, Autism was considered to be a mental illness or emotional maladjustment. However nowadays experts believe that it is a biological disorder. What it means is that it is due to organic causes rather than psychological.
To be more specific, autism is a neurological or developmental brain disorder caused by biological reasons resulting in problems in cognition, communication, and interaction. The onset of Autism typically occurs before three years of age.
It is an irony that despite the consensus of biological causality, autism is still classified as a mental disorder in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-Fourth Edition (DSM-IV). In my experience I have seen that many children with autism suffer from several biological issues such as:
- Food allergies
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Intestinal overgrowth of Candida Albicans
- Impaired immunity
- Thyroid malfunction
- Malnutrition
Autism may not be genetic in Nature
Several health care practitioners claim that Autism is genetic. Well, it is easy to label it genetic, however, please note that incidence of autism is increasing over the years. In last 15 years there has been 1000% increase in incidence of autism. Incidence of genetic disorders remains stable over time, however this increase means that autism is much more the a genetic disorder. Or as most suspect, it may have nothing to do with genetics at all! And that is good news because there is not much one can do with a genetic defect. But if it is not a genetic defect, then there is the possibility of recovery! Hallelujah!
A good news for parents of children with Autism
Dear parents, if your child is diagnosed with Autism, I would like to tell you that it is not the end of the world. Several parents including Jenney McCarthy have documented that it is possible to Recover your child’s life from Autism.
So please don’t accept that you can not do anything about autism. You need to follow a multidisciplinary remedial intervention to help them live happily with their limitations. To do so, you need to understand the imbalances in their body due to nutritional deficiencies and correct them. It has been found that with such therapies, impact of autism can be reduced or reversed to a great extent.
Get ready to recover his life
Prepare for the research of your life. This article could be your starting point. I will share all the possible approaches you can follow here. Feel free to ask questions and I will try my best to answer them.
Your child is unique. Therefore his treatment will also be unique. His therapy needs to be tailored to his individual needs. There is no generalized treatment for children with autism. Children with Autism have several common contributing factors, but the imbalances created by these factors may not be same.
As parents, you are in the best position to decide what is right for him. Just to a good start here are few steps you must take in your journey to recover your child from Autism.
A child with autism has a pure mind and heart, every action you take will result in a change in his behaviour. Close observation will be your guide to decide what is right and what is working for him.
I hope I have answered some of your questions, if you have more, please leave them below or connect with us now.
Sources
- http://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/autism/index.html, extracted & modifies on 14 Aug 2016.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder – https://csd.wisc.edu/slp-autism-spectrum-disorder.htm, extracted & modifies on 14 Aug 2016.
- Rett Syndrome – http://www.rettsyndrome.org/about-rett-syndrome/what-is-syndrome, extracted & modifies on 14 Aug 2016.



Hello Anupama, you are doing such a great work. This is such an informative article which is really helpful for the parent to know about Autism. I would also suggest everyone that if we found any warning signs of the developmental delay in children as a responsible parent we should not follow the wait and watch approach. We should consult with the developmental pediatrician/ early intervention specialist at the right time and treat the delays before it’s too late.