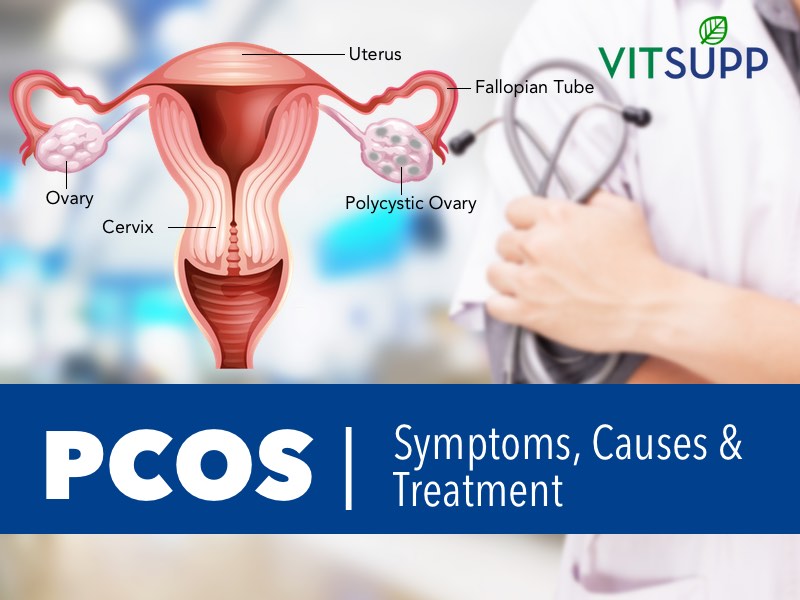
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome commonly known as PCOS, is a prevalent reproductive disorder in women. PCOS is the leading cause of infertility among women today.
PCOS is characterised by:
- Hormonal imbalance with the overproduction of the androgen hormone testosterone.
- Menstrual abnormalities
- Enlarged ovaries containing multiple immature follicles (cysts).
Women with severe PCOS have
- Greater menstrual irregularity
- Androgen excess
- Abdominal fat
- Resistance to insulin
- Severe risk factors for diabetes and cardiovascular disease than women with less severe forms of PCOS.
Research has showed that polycystic ovary syndrome is more prevalent among family members than in the general population, suggesting that genes are a factor in the development of PCOS.
Lifestyle habits, including diet and exercise, also affects the severity of PCOS. Weight gain worsens the reproductive and metabolic abnormalities in women with this disorder.
Contents
What is PCOS?
PCOS is a hormonal imbalance problem that affects women during their childbearing years (ages 15 to 44). Between 2.2 and 26.7 percent of women in this age group have PCOS (1, 2).
PCOS in India
Metropolis Healthcare Ltd, conducted a comprehensive pan India study on 27,411 samples of testosterone over a period of 18 months. Out of 27,411 samples, around 4,824, (17.60%) of the females face hormonal associated risk with polycystic ovarian syndrome. Among the samples tested East India shows alarming levels of 25.88% women affected by PCOS, followed by 18.62% in North India, 20% in West India and 18% in South India. (3)
Many women have PCOS but don’t know it. In one study, up to 69 percent of women with PCOS hadn’t been diagnosed (1).
What is Ovulation
Ovaries are the reproductive organs of a woman. They produce oestrogen, progesterone and also small amounts of male hormones called androgens in a certain proportion. PCOS affects the ovaries in such a way that the production of these hormones becomes unbalanced.
The ovaries of a woman, release eggs to be fertilized by a male sperm. The release of an egg each month is called ovulation.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) control the ovulation. FSH stimulates the ovary to produce a follicle (egg sac) and then LH triggers the ovary to release the egg when it matures.
Polycystic ovarian disease
PCOS is a syndrome that affects the ovaries and ovulation due to hormonal imbalance. Its three main features are:
- cysts in the ovaries
- high levels of male hormones
- irregular or skipped periods
In PCOS, many small, fluid-filled sacs grow inside the ovaries. The word “polycystic” means “many cysts.”
These sacs are actually follicles, each one containing an immature egg. The eggs never mature enough to trigger ovulation.
Women with PCOS have altered levels of estrogen, progesterone, FSH, and LH. Estrogen and progesterone levels are lower than usual, while androgen levels (the male hormones) are higher than usual.
Extra male hormones disrupt the menstrual cycle, so women with PCOS get fewer periods than usual.
PCOS was first described by Italian physician Antonio Vallisneri fn 1721 (4).
Your Takeaway:
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) affects up to almost 27 percent of women during their childbearing years (5). It involves cysts in the ovaries, high levels of male hormones, and irregular periods.
Polycystic Ovarian syndrome causes
Researchers have not been able to find the exact causes of PCOS, due to the nature of the disorder. The severity of PCOS varies greatly region wise, depending on may factors such as genes, hormonal imbalance, lifestyle habits and diet.
Medical researchers and doctors believe that the immediate cause of cyst formation in enlarged ovaries is the excess production of the male androgen hormone testosterone.
Excess androgen hormone production in women of childbearing age has been attributed to Genes, insulin resistance, inflammation, exposure to plastics.
1. Genes
Polycystic ovary syndrome is more prevalent among family members than in the general population, suggesting that genes can influence the development of PCOS.
Although the genetic role in this disorder is not completely clear, multiple genes -not one- contribute to the problem. (6, 7, 8, )
2. Insulin Resistance a leading cause of PCOS
Insulin is a hormone that helps the body absorb glucose, keeping blood sugar levels in balance. Therefore, Insulin resistance makes it harder for glucose to be absorbed, causing sugar buildup in the blood.
Upto 70 percent of women with PCOS have insulin resistance.
A study found that excess insulin appears to be an important factor in maintaining hyperandrogenemia, acting directly to induce excess androgen production. (9)
In other words, excess insulin production in the body causes the ovaries to produce higher levels of male androgen hormone – testosterone.
Obesity, driven by bad eating habits and lack of exercise, is a major cause of insulin resistance. High insulin resistance increases the risk of developing PCOS.
3. Inflammation
A study conducted at the Indiana University School of Medicine, has found that chronic low-grade inflammation has emerged as a key contributor to the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
The study also noted that a dietary trigger such as glucose(sugar) is capable of inciting oxidative stress and an inflammatory response from mononuclear cells (MNC) of women with PCOS. This phenomenon is independent of obesity. (10)
In simple words the study states that foods that convert into glucose quickly are the culprit in creating a chronic inflammation condition in women with the PCOS disorder.
Being overweight also contributes to inflammation.
Studies have linked excess inflammation to higher androgen levels.
4. Plastic Exposure: An ignored cause of PCOS
It’s been known for decades that BPA (Bisphenol-A) found in household plastics has estrogenic activity. New research has now found that not only does BPA have a large impact on PCOS, it may even be a cause of it.
One study found that women with PCOS have 30-40% more BPA in their blood compared to women without PCOS. Another study in rats found that exposure to BPA in the womb leads to PCOS development in later life. (11, 12)
BPA impacts PCOS by increasing the amount of androgens in our blood.
It does this in three main ways:
1 BPA Stimulates The Ovaries To Produce More Androgens
PCOS is a syndrome of many symptoms, however high androgenic activity, including testosterone – is the mainstay of this disorder.
Male pattern balding, facial hair and acne are some of the red flags caused by excess levels of androgens.
Androgens are produced by the theca cells in our ovaries. Studies have shown that BPA causes these cells to significantly increase androgen production. (13, 14)
2 BPA binds to receptor sites for sex hormones.
Free sex hormones like testosterone are bound to the Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG) to prevent them from roaming free and causing hormonal imbalance in the body.
The problem with BPA is that because it has the same structure as sex hormones it mimics the activity of testosterone. The BPA in the body binds to the receptor sites of SHBG and the testosterone then has nothing to bind to.
Animal studies have shown that BPA displaces testosterone and androgens at receptor sites, increasing the amount roaming free in the blood. (15)
3. BPA Increases Inflammation And Overloads The Liver
Studies have shown that women with PCOS have high levels of both BPA and teststerone. (16, 17)
The liver is the main detoxifying organ of our bodies and it is unable to cope with high levels of both.
Studies have also shown high levels of inflammation markers suggesting that BPA in the liver causes low grade inflammation.
Inflammation, of course, is one of the main causes of PCOS.
Symptoms
Girls may sometimes notice symptoms during around their first period, even then PCOS usually goes undiagnosed. For most women though, PCOS comes into picture when they have trouble getting pregnant.
The most common PCOS symptoms are:
- Irregular periods:The lack of ovulation due to hormonal imbalance prevents the uterine lining from shedding every month. Menstrual disorders can include absent periods, periods that occur infrequently or too frequently, heavy periods, or unpredictable periods. Some women with PCOS have fewer than eight periods in a year. Or, their periods may come every 21 days or more often.(18).
- Heavy bleeding:The uterine lining may build up for a longer period of time, so the periods may be heavier with clots than normal.
- Hair growth:More than 70 percent of women with this condition grow hair on their face and body — including on their back, belly, thigh and chest (19). This excessive hair growth is called hirsutism.
- Acne:Male androgen hormones can make the skin oilier than usual and cause breakouts on areas like the face, chest, and upper back. This acne unrelated to adolescence and does not respond to the usual treatments.
- Obesity:Up to 80 percent of women with PCOS are overweight or obese (20).
- Male-pattern baldness:Women with PCOS may suffer from mail pattern baldness where the hair on the scalp gets thinner and falls
- Darkening of the skin:Dark patches of thickened, velvety, darkened skin can form in body creases like those on the neck, in the groin, and under the breasts.
- Headaches:Hormone imbalances can trigger headaches in some women.
- Cysts in the ovaries : Fluid filled immature follicles form cysts in the ovaries.
How PCOS affects the body
The presence of high levels of androgen hormones like testosterone can not only cause infertility, but also affects other aspects of you life. Here are some conditions that are impacted by PCOS:
1. Infertility
To get pregnant, you have to ovulate. Women who don’t ovulate regularly release much fewer eggs to be fertilized. PCOS is one of the leading causes of infertility in women (21).
2. Metabolic syndrome
Up to 80 percent of women with PCOS are overweight or obese (22). Studies have found a high correlation between PCOS and insulin resistance. Both obesity and PCOS increase your risk for high blood sugar (type 2 diabetes), high blood pressure and cardiovascular problems.
Together, the factors impacting high blood sugar, high blood pressure, inflammation related cholesterol problems are called the metabolic syndrome.
3. Sleep apnea
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts.
It is more common in women who are overweight — especially if they also have PCOS. The risk for sleep apnea is 5 to 10 times higher in obese women with PCOS than in those without PCOS (23).
4. Endometrial cancer
During ovulation, the uterine lining sheds every month. However if due to polycystic ovaries, you don’t ovulate every month, then the lining can build up – causing the uterine lining to thicken.
And a thickened uterine lining can increase your risk for endometrial cancer (24).
5. Depression
Hormonal changes in PCOS can cause mood swings. Also symptoms like unwanted hair growth can also negatively affect your emotions.
Approximately 34% of women with PCOS have depression compared to 7% of women in the general population and around 45% have anxiety, compared to only 18% of the general population.
Studies show there is a strong link between excess androgen, insulin resistance, and PCOS depression (25).
PCOS Diagnosis
PCOS can adversely impair a woman’s health by increasing her risks for infertility, obstetrical complications, diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
While there is no test to definitively diagnose PCOS. Your doctor enquire after your medical history, including your menstrual periods details and weight changes. A physical exam will include checking for signs of excess hair growth, insulin resistance and acne.
Your doctor might recommend the following:
- A pelvic exam.The doctor visually and manually inspects your reproductive organs for abnormal growths or swelling.
- Blood tests.Your blood may be analyzed to measure hormone levels. This testing can exclude possible causes of menstrual abnormalities or androgen excess that mimics PCOS. Doctor might also recommend measuring glucose tolerance and fasting cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
- An ultrasound.The doctor may recommend checking the appearance of your ovaries and the thickness of the lining of your uterus.
These are very useful, as diagnosing PCOS depends upon identifying whether a woman has
- Androgen excess,
- Disorders of ovulation and/or
- Polycystic ovaries,
while eliminating other illnesses that mimic PCOS.
PCOS and Pregnancy
PCOS is the leading cause of infertility in women of child bearing age. 80 percent of women suffering from PCOS have fertility problems due to hormonal imbalances. (26)
Besides this the women who do get pregnant may face other pregnancy complications. For instance, women with PCOS are twice as likely as women without the condition to deliver their baby prematurely.
They’re also at greater risk for miscarriage, high blood pressure, and gestational diabetes (27). However, women with PCOS can get pregnant using fertility treatments that improve ovulation.
Also Losing weight and lowering blood sugar levels can improve your odds of having a healthy pregnancy.
PCOS Natural Treatment : Diet Plan & lifestyle
The good news is that for many PCOS can be naturally reversed. While medical experts still do not state the clear reasons of PCOS/PCOD. Data from research is clear. Insulin resistance is the key to these ovarian health problems..
Read More : Can My Diet Treat Symptoms of PCOS?
Reversing PCOS: Insulin Resistance Is The Key
You can be insulin resistant for years without knowing it. Unfortunately insulin resistance does not trigger any noticeable symptoms. While a full blown case of insulin resistance may lead to diabetes, not all people with insulin problems may progress to diabetes instantly.
In other words, your genes will determine how your body will react to a toxin/environmental insult / wrong diet & lifestyle habits.
For a large number of women with PCOS, insulin resistance is the key to their condition (9)
If you’re insulin resistant, your body may try to pump out high levels of insulin in an effort to keep your blood sugar levels normal.
Too-high levels of insulin can cause your ovaries to produce more androgen hormones, such as testosterone.
The good news: Insulin resistance is caused by wrong diet & sedentary lifestyle. Insulin resistance is reversible for most.
Diet & Lifestyle Changes: Key to managing insulin resistance
Diet & exercise are the key to reversing PCOS by managing insulin resistance.
80% of women with PCOS have found to be overwieght or obese. Losing weight will not only reduce insulin and androgen levels, it will also restore normal ovulation.(22)
Leading a healthy lifestyle that depends on eating a clean, healthy Low Carb & High Fat (LCHF) diet and focuses on getting regular exercise. Improving you insulin-sensitivity is a long-term fix that will also improve your odds of getting pregnant.
A healthy lifestyle will also improve your quality of life, making you feel stronger, fitter, happier with improved cognitive abilities.
Three Steps To Reverse PCOS Naturally
1. Switch To A Low Carb High-Fat Diet
Duke University Medical Center has conducted research to study the effects of a low-carbohydrate, high fat diet on reversing PCOS. And researchers found that such a diet led to significant improvement in weight, percent free testosterone, fasting insulin in women with obesity and PCOS over a 24 week (6 months) period. (28)
Read More : Can My Diet Treat Symptoms of PCOS?
2. Exercise Regularly to Reverse PCOS
Exercise improves insulin resistance. Any kind of exercise will work. Muscle and weight training workouts to build lean muscle mass and help the body become more sensitive to insulin. However, cardio workouts are the key to losing weight, so work both kinds of exercise in your routine.
3. Dietary Supplements For PCOS
When attempting to reverse PCOS through diet and exercises, some supplements can be your friends. When chosen correctly, the right dietary supplements can support your body’s ability to use insulin and can help keep your blood sugar stable.
- For Inflammation: Turmeric (Curcumin) & Vitamin D3
- For Insulin sensitivity: Cinnamon, Indrajow
- Others: Omega 3 (fish oil) & magnesium
Medical treatments
There are many medical options to treat polycystic ovarian disease or PCOD under the doctors supervision.
1. Birth Control
Birth Control Pills are often prescribed to treat polycystic ovary symptoms like hormonal imbalance, hair growth and acne. Women with polycystic ovary syndrome often do not have regular menstrual periods. Birth control pills can restore the mentrual cycle to normalcy.
This option is great for the treatment of polycystic ovarian syndrome if you do not want to become pregnant.
Birth control pills can restore your periods to normal, ensuring that the uterus lining is shed every month. Timely shedding of the uterine lining reduces its risk of thickening consequently reducing the risk of endometrial cancer.
2. Metformin
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a common endocrine disorder with reproductive and metabolic complications. Insulin resistance and secondary hyperinsulinemia affect approximately 65-70% of women with this condition.
Metformin is used to treat Type-2 diabetes patients. It helps with controlling blood sugar levels and increases the sensitivity of the cells to insulin.
Due to insulin resistance, women with PCOS produce higher levels of insulin than they otherwise would have. This in turn prompts the ovaries to produce higher amounts of testesterone which may lead to infertility, obesity, hirsutism and acne. (29)
One study found that taking metformin in addition to diet and exercise changes, improves weight loss, lowers blood sugar, and restores the normal menstrual cycle better than lifestyle changes alone (30).
Metformin(glucophage) is available as 500mg, 850mg, and 1000mg tablets with a target dose of 1500-2550 mg per day. Many studies in PCOS have used a dose of 850 mg twice a day for 6 months.(31) It can be an alternative to oral contraceptives for treatment of polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Side effects of metformin are mainly gastrointestinal such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, bloating, flatulence etc.
3. Clomiphene
Clomiphene citrate is an ovulation inducing fertility drug. It is used to treat irregular or absence of the menstrual cycle.
It works by increasing the progesterone secretion during the second half of the menstrual cycle and to make it longer & more predictable. It increases the progesterone by stimulating the brain’s pituitary gland to secrete an increased amount of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and LH (luteinizing hormone).
This further stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles, thus initiating ovulation.
During a normal cycle only one egg is ovulated. Clomiphene may cause the ovaries to produce two or three eggs per cycle.
It is usually taken orally for 5 days and is active only during the month it is taken. If 2 weeks after ovulation, pregnancy does not occur, menses will occur. Clomiphene may then be administered again in the next cycle on a higher dose.
It can be used alone or may be combined with metformin. One study has found that clomiphene is superior to metformin in achieving live birth in infertile women with the polycystic ovarian syndrome, although multiple births may be a complication. (32)
Clomophene is a tried and trusted, safe, effective fertility drug that is relatively low cost.
4. Surgery
1. Ovarian Drilling
Women with pcos have ovaries with thick outer layer which causes them to produce too much testosterone resulting in irregular or absent periods.
Ovarian drilling works by disturbing the thick outer lining of the ovaries resulting in lower testosterone production.
This can help restart regular monthly periods and result in timely ovulation. Ovarian drilling is done by a minimally invasive surgery called laparoscopy
2. In-vitro Fertilization (IVF)
When normal ovulation and fertilization fails, then doctors may recommend in-vitro fertilization. In this process the doctor takes the eggs and the sperms in a lab, out of the body.
The fertilization of the eggs is done in the lab and then one or more fertilized eggs (embryos) are put in the uterus. Pregnancy happens if any of the embryos implant successfully in the lining of the uterus.
Related Article : PCOD Problem – Solution and Treatment
Related Article : Urine Infection in Women – 16 Tried Home Remedies
FAQ’s
Q1 What is pcos meaning?
Ans: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disorder that affects a woman’s hormone levels. Women with PCOS produce excess amounts of androgen male hormones. This hormone imbalance leads to fewer, or even no menstrual periods and making it harder for women with PCOS to get pregnant.
Q2 How to cure pcos permanently
Ans: Your doctor may offer different medicines that can treat symptoms such as irregular periods, acne, excess hair, and elevated blood sugar. Primarily, additional hormones are used to treat these symptoms. Fertility treatments like IVF are also available to help women get pregnant. Treatment for PCOS usually starts with lifestyle changes like weight loss, diet, and exercise. Some ways to lessen and even reverse PCOS symptoms are:
- Losing as little as 5% excess weight can help women ovulate more regularly and lessen other PCOS symptoms.
- 70% of women with PCOS have insulin resistance. You need to avoid all foods that convert to glucose quickly. White flour, rice, packaged foods, sweets, sugar and for people with sever issues even fruit. Alternatively talk to your doctor about Metformin.
- Regular exercise allows better health and reduces the impact of PCOS.
- Avoid eating and storing food and beverages in plastic containers to avoid BPA.
While there are no studies to confirm this, however, anecdotally some women have reported losing their PCOS diagnosis in 4-6 months with lifestyle and diet changes.
Q3 What is the difference between pcos and pcod
Ans: They are both associated with symptoms like irregular periods common to both. Other symptoms are adult acne, hirsutism and male pattern hair loss. They are caused by hormonal imbalance; and contribute to infertility. However PCOS is much more severe than PCOD. PCOS is a more severe form of the polycystic syndrome.
Q4 How to cure pcos naturally fast
Ans: Weight reduction has been shown to normalize ovulation, improve hyperandrogenism, and increase rates of conception in women with PCOS.
Reducing weight & improving insulin sensitivity is the key to treating this condition. This can be done by diet changes and exercise. Or by medical treatments such as metformin, oral contraceptives, Clomiphene, Ovarian drilling or IVF.
This article talks about the pcos diet.
Q5 What is ramdev baba yoga for pcos in hindi
Q6 What is polycystic ovaries meaning
Q7 Why getting pregnant with pcos after 30 is difficult
Q8 What is pcos meaning in hindi
Q9 how to get pregnant with pcos problem in hindi
Q10 how to get pregnant with pcos and irregular periods
Q11 what is pcos treatment to get pregnant
Q12 What are symptoms of pcos in females
Q13 how to get pregnant with pcos quickly
Q14 how to cure pcos naturally and get pregnant
Q15 how to get rid of pcos completely
Q16 What are pcos home treatment
Q17 What is pcos treatment in patanjali
Q18 Can I take ashokarishta for pcos
Q19 Which is the best exercise for pcos to get pregnant
Q20 how to get regular periods with pcos naturally
Q21 What is ayurvedic treatment for pcos at home
Q22 What is the ovary size in pcos
Q23 Which are natural remedies for pcos getting pregnant
Q24 Which are the 5 types of pcos
Q25 how to cure pcos naturally in tamil
Q26 pcos treatment in ayurveda in hindi